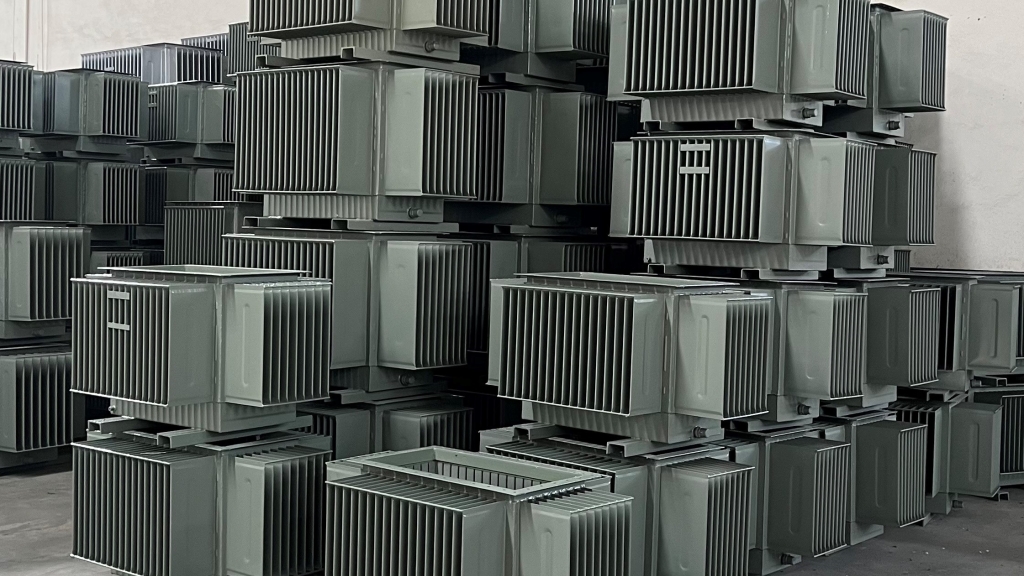
Construction
In the oil immersed transformer tanks, core is inside the transformer cooling oil. Transformer tank provides isolation of oil and the core from outside environment and used for cooling process.
The most of distribution transformer tanks are produced with cooling fin as corrugated walls or radiators. The aim of cooling fins is to increase contact area with the atmosphere. In addition, in hermetic type designed transformer tanks, the corrugated walls permit a level of elasticity which is essential to provide volume change of isolation oil as it heats and cools, in connection with load and ambient temprature. This provides the tank to be totally filled (and hermeticaly sealed), with the significiant advantage of extending the transformer’s service time and reducing maintenance expencies.
In special conditions, forexample small ratings or severe dimensional limitations, the corrugated walls can be ver small that they don’t meet flexiblity enough, requiring the use of a gas storage to allow the expansion of the isolation oil. This gas storage makes stable the internal pressure within the acceptable limits permitted by tank flexibility. Sometimes, a conservator is fitted on top of the transformer tank to act as an expansion tank for isolation oil. The conservator is often fitted with a oil level indicator, an air vent and an air dryer (dehumidtifier) in an effort to ensure that only dry air can come into contact with the cooling oil, and only at atmospheric pressure. If the air dryer is not properly maintained, it can lose its effectiveness and allow damp air to come in contact with the cooling oil.
Functions of the transformer tank:
- Forming a container for the cooling oil.
- Acting as a heat exchanger for heat losses.
- It is a protective, earthed safety shell.
- Providing shielding against electromagnetic field leakage
Cooling
Heat is generated inside a transformer by the effects described by Joule’s law, hysteresis losses and eddy currents. This causes a rise in the temperature of the windings and core. The temperature will reach equilibrium when the quantity of generated heat is equal to the quantity of removed heat.
Cooling is optimized in accordance with the maximum permissible temperature of the insulation system and the total quantity of heat to be dissipated, which depends on the transformer’s loss level
Transformer tank types according cooler types:
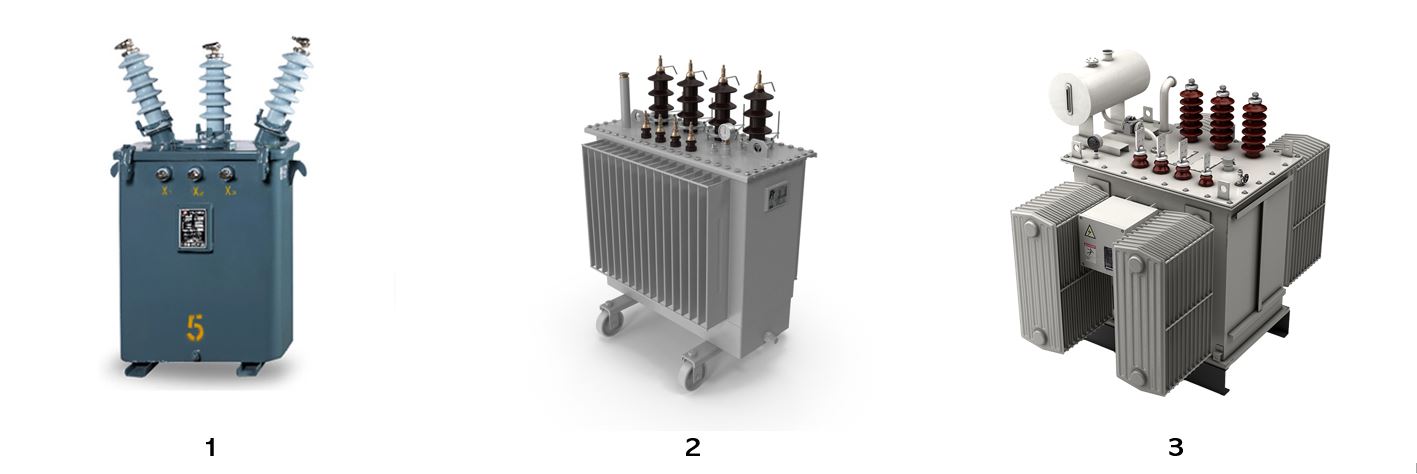
- Transformers without cooling
- Corrugated wall type transformers
- Radiator type transformers
Transformer tanks according oil dilataion:
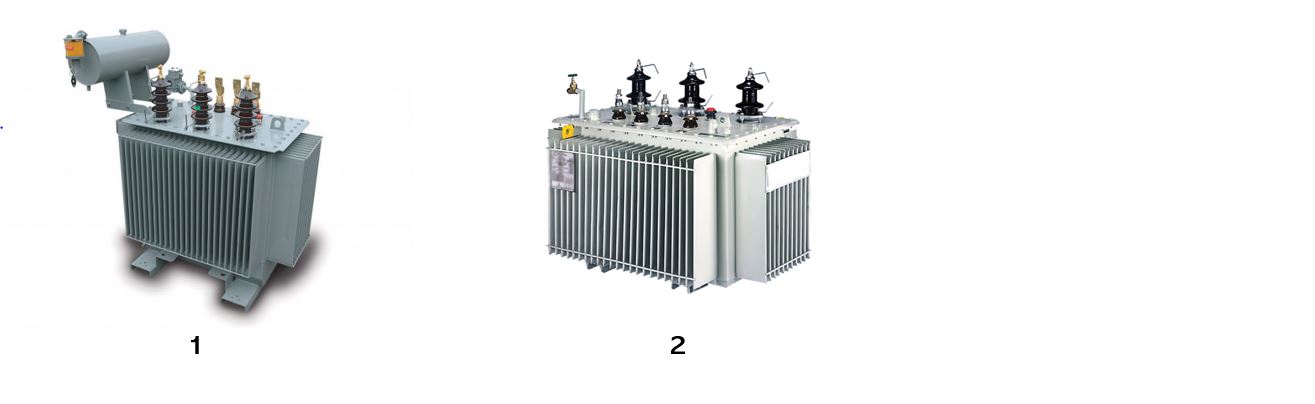

- Tanks with reserving tubes
- Hermetic type transformers